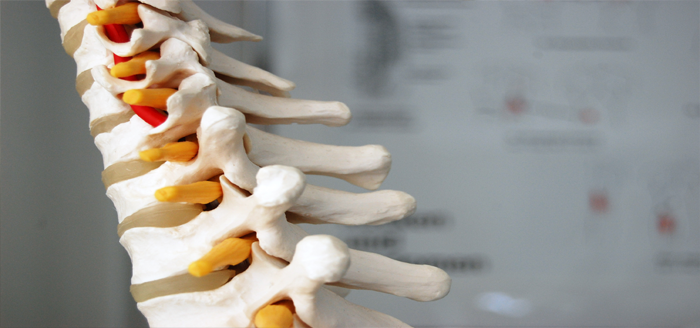
Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)
Degenerative disk disease, or DDD, is the result of normal changes occurring overtime in the discs of the spine that result in pain or discomfort.
Spinal discs are located between each vertebrae of the spine. These discs function like tiny shock absorbers, allowing the spine to bend and flex while protecting against pain and injury. Over time, and as we age, these discs start to break down. While not everyone experiences pain from worn down spinal discs, those who do are often diagnosed with degenerative disc disease.
Causes of Degenerative Disk Disease
Although not technically considered a disease, degenerative disc disease is a condition that occurs when the discs of the spine begin to breakdown; causes of DDD include :
- Normal changes associated with aging;
- Drying out of spinal discs, reducing the amount of protection provided;
- Sports or work-related activities or injuries that cause discs to herniate, tear, or rupture;
Spinal discs have little access to consistent blood supply; unlike other organs of the body, once injured or damaged, the disc cannot heal itself and begins to deteriorate.
Symptoms
Symptoms of DDD are most often found in the lumbar (low back) or cervical (neck) area of the spine; the most common symptoms associated with degenerative disc disease include:
Pain that can range in intensity from minor to debilitating
Numbness, discomfort, or pain that radiates to the legs, feet, arms, or hands
Discomfort that intensifies while sitting
Pain that becomes more intense when bending, twisting, or lifting an object
Discomfort, pressure, or pain that becomes less intense while moving, walking, or lying down
Diagnosis
DDD is generally diagnosed after a physical assessment and complete review of medical history, including detailed descriptions of the specific symptoms being experienced and the exact circumstances leading up to the onset of the pain and discomfort.
Possible Treatments
The most effective and longest-lasting treatment for back pain, including DDD, is increasing the strength and flexibility of the muscles associated with spinal support. In addition to exercises and stretching designed to increase strength and flexibility of muscles in the back, treatment for degenerative disc disease may include: